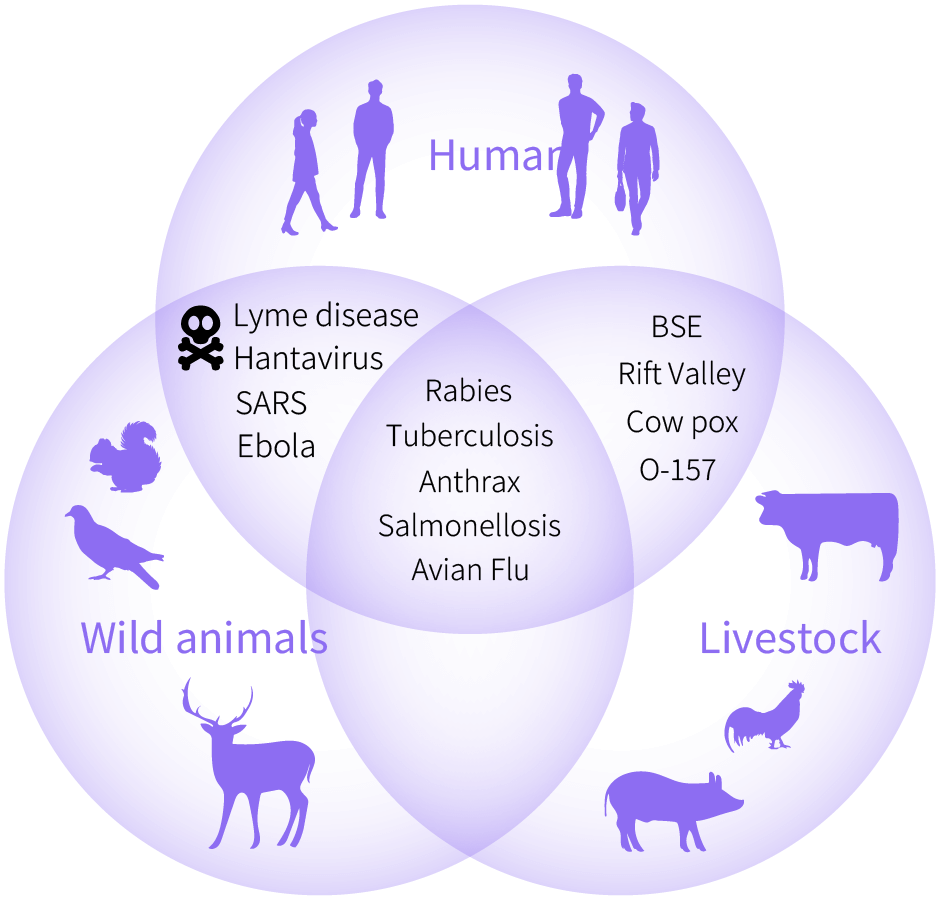
Controlling Viral Infections Across Species Barriers
Many pathogens mainly circulate in certain animal species that serve as their natural hosts. However, some pathogens, such as influenza viruses and SARS-CoV-2, which cause zoonotic diseases, acquire adaptive mutations that enable them to overcome species barriers, spillover from wildlife and livestock to humans, and trigger global pandemics as emerging infectious diseases. To prepare for future pandemics, continuous surveillance of viral mutations and understanding the mechanisms by which viruses adapt to humans are crucial. Our goal is to elucidate the molecular basis of how viruses adapt to humans and express viral pathogenicity by uncovering the mechanisms that allow viruses to efficiently replicate in host cells and evade host immunity, particularly inflammatory responses.
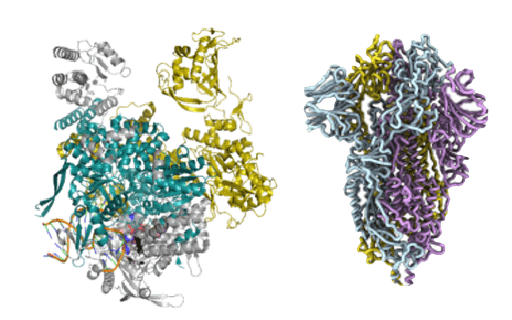
Viral RNA synthesis by viral polymerases
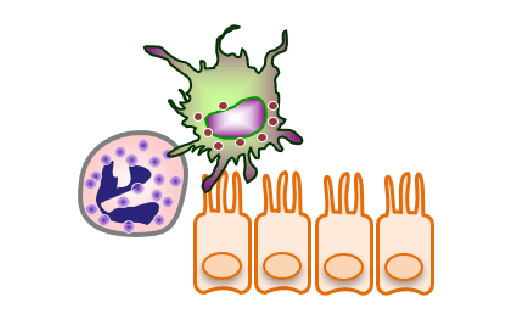
Innate immunity and stress responses against viral infection
Intracellular transport of viral proteins
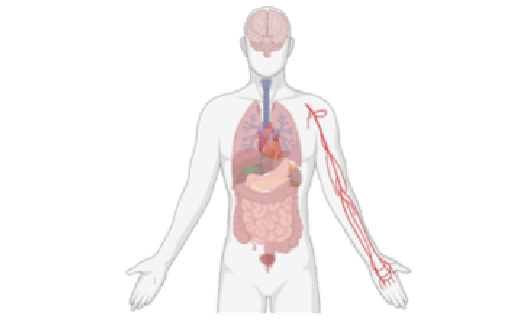
Multi-organ infections
二Secondary bacterial pneumonia

Exacerbation of viral pathogenesis by inflammaging
Adverse reactions to vaccines
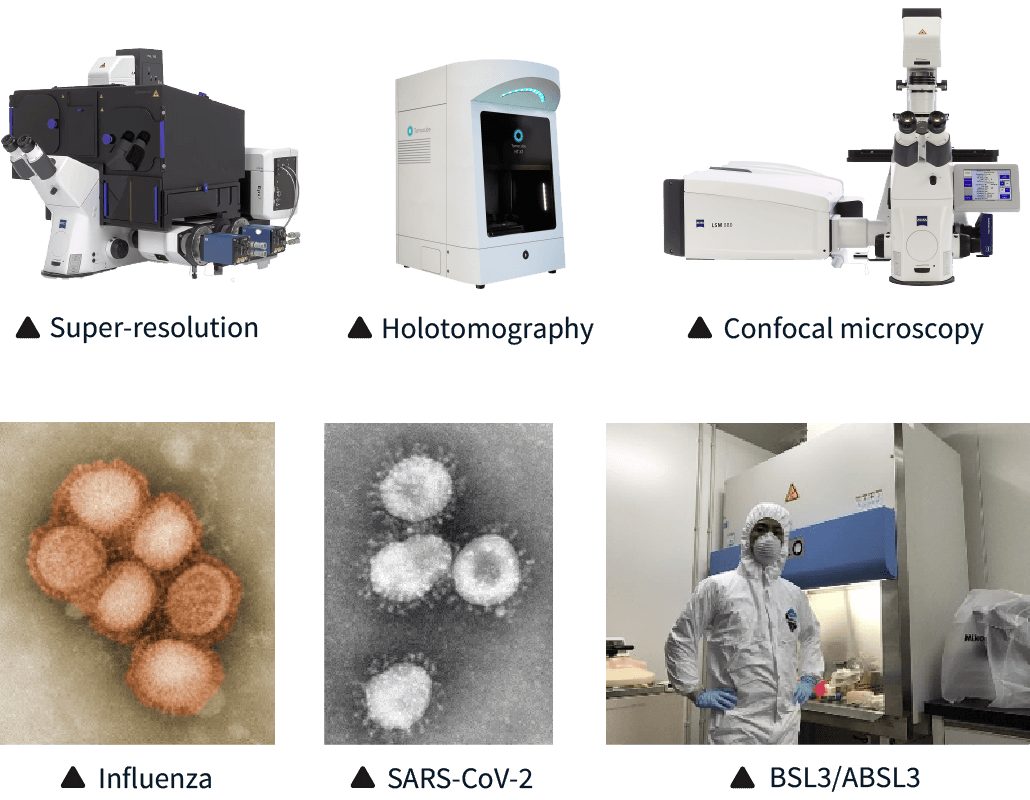
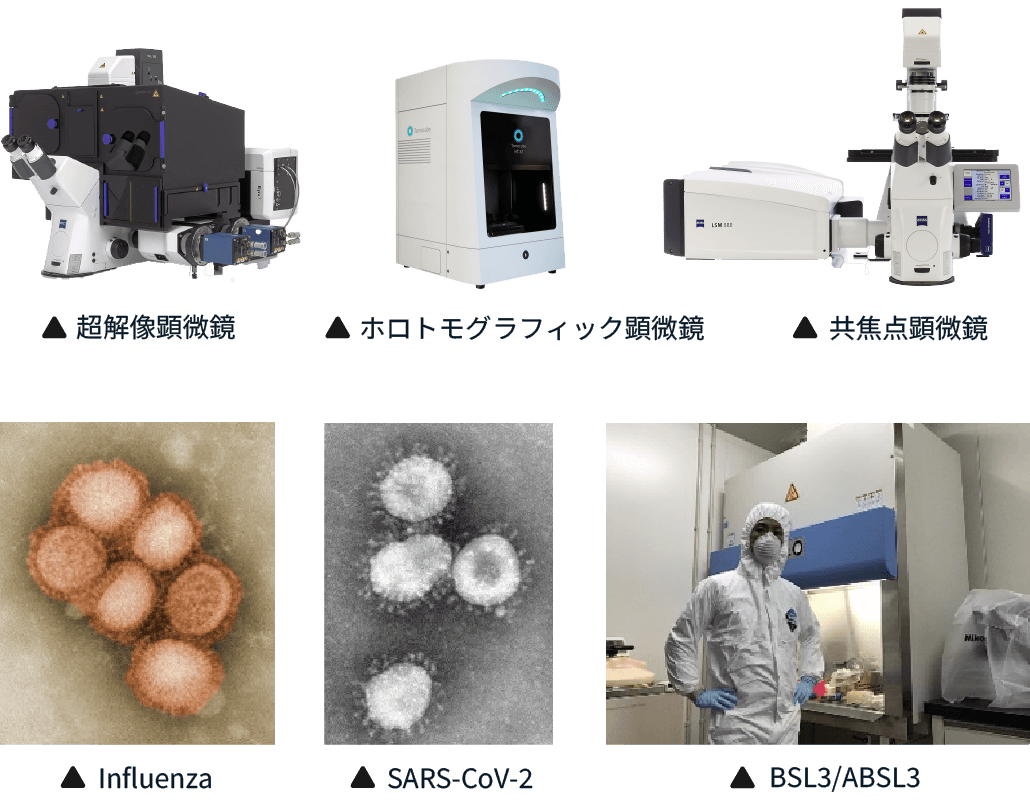
In our laboratory, we are advancing research with an integrated approach that spans multiple levels, from molecular to organ and individual levels, to uncover the molecular basis of infectious diseases. We employ cutting-edge optical microscopy for cell biological analyses, work with high-pathogenic strains in BSL3 facilities, establish infection animal models using gene editing techniques, and analyze clinical samples in collaboration with the University of Tsukuba Hospital. Through this multifaceted approach, we are driving forward infectious disease research.

取り組んでいる研究The research we are working on
-
ウイルスの宿主適応と複製機構の解析 Adaptation of Emerging Viruses to Humans宿主に依存したウイルス複製機構の解明 ウイルスはゲノムサイズが小さいため、遺伝子数が限られます。 そのため、ウイルスは宿主の因子を強奪することで複製しており、新しいウイルスがヒトへの感染能を獲得するには、ヒトの宿主因子に適応することが必要です。 私たちのグループではウイルスの複製に必要な宿主タンパク質の同定と機能解析をめざしています。 Adaptations...Understanding host-dependent replication of viruses Viruses have limited genetic information due to their small genome. Over the years, our group focuses on the identification of host proteins required for virus replication.
-
ウイルス感染により引き起こされる病態の解明 Understanding How Viruses Cause Severe Symptoms in Humansウイルス感染症の重症化機構の解析 病原性細菌とは異なり、ウイルスは毒素遺伝子をもちません。 どのようにウイルスは人に重篤な症状を引き起こすのだろう? Multi-organ failure induced by viremia SARS-CoV-2を含む、一部の呼吸器感染症ウイルスは肺胞から血中に侵入し、多臓器感染を引き起こします。 ウイルスはどのように基底...Mechanism of the Development of Viral Pathogenesis In general, no toxins are encoded in viral genome, unlike pathogenic bacteria. It is unclear how viruses cause severe symptoms in humans but not their nature hosts. Multi-orga
-
ウイルス感染による常在細菌叢の変容 Out of Control of Commensal BacteriaActivation of commensal bacteria by virus infection 常在細菌は人に害を与えることなく、場合によっては体に利益をもたらして共生しています。しかし、インフルエンザウイルス感染を要因として、下気道で常在菌が異常増殖し、二次性細菌性肺炎を引き起こします。 ウイルスと常在細菌はどのように相互作用するのだろう? わかっ...Activation of commensal bacteria by virus infection Commensal bacteria live in our body without causing harm or providing direct benefits. But, influenza virus infection triggers abnormal growth of commensal bacteria in lower respiratory tr
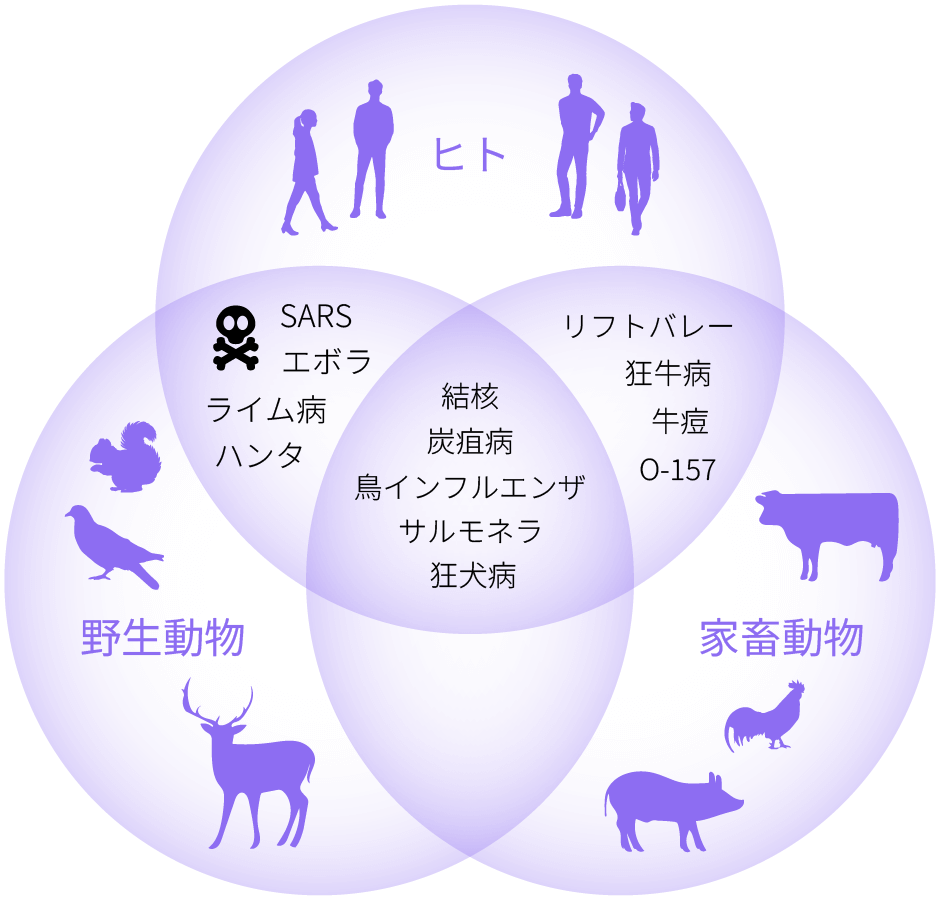
種の境界を超えるウイルス感染症を制御する
インフルエンザウイルスやSARS-CoV-2など、人獣共通感染症を引き起こす病原体は、適応変異により、種の壁を越え、野生動物や家畜から人類に伝播し、パンデミックをひきおこします。将来的なパンデミックに備えるためには、病原体の変異追跡による継続的な監視と、その変異によってウイルスが人類に適応するメカニズムの解明が求められています。私たちは、適応変異を獲得することで、ウイルスが宿主細胞を利用して効率よく複製するメカニズムと、炎症応答を中心とした宿主免疫を回避するメカニズムを明らかにし、ウイルスが人類に適応し、病原性を発現する分子基盤の理解をめざしています。

ウイルスRNA合成機構

ウイルス感染に対する自然免疫応答やストレス応答
ウイルスタンパク質の細胞内輸送機構

多臓器感染による病態発現機構
二次性細菌性肺炎の発症機構

炎症老化による感染病態の増悪機構
ワクチンによる副反応の発症機構
私たちの研究室では、分子レベルから臓器・個体レベルまで、階層を超えた統合的アプローチで感染症研究を推進しています。最先端の光学顕微鏡を用いた細胞生物学的解析や、BSL3施設での高病原性株を使用した研究、遺伝子改変技術を用いた感染動物モデルの構築、さらには筑波大学附属病院と連携した患者検体を用いた解析など、多角的な手法を駆使した感染症研究に取り組んでいます。

取り組んでいる研究The research we are working on
-
ウイルスの宿主適応と複製機構の解析 Adaptation of Emerging Viruses to Humans宿主に依存したウイルス複製機構の解明 ウイルスはゲノムサイズが小さいため、遺伝子数が限られます。 そのため、ウイルスは宿主の因子を強奪することで複製しており、新しいウイルスがヒトへの感染能を獲得するには、ヒトの宿主因子に適応することが必要です。 私たちのグループではウイルスの複製に必要な宿主タンパク質の同定と機能解析をめざしています。 Adaptations...Understanding host-dependent replication of viruses Viruses have limited genetic information due to their small genome. Over the years, our group focuses on the identification of host proteins required for virus replication.
-
ウイルス感染により引き起こされる病態の解明 Understanding How Viruses Cause Severe Symptoms in Humansウイルス感染症の重症化機構の解析 病原性細菌とは異なり、ウイルスは毒素遺伝子をもちません。 どのようにウイルスは人に重篤な症状を引き起こすのだろう? Multi-organ failure induced by viremia SARS-CoV-2を含む、一部の呼吸器感染症ウイルスは肺胞から血中に侵入し、多臓器感染を引き起こします。 ウイルスはどのように基底...Mechanism of the Development of Viral Pathogenesis In general, no toxins are encoded in viral genome, unlike pathogenic bacteria. It is unclear how viruses cause severe symptoms in humans but not their nature hosts. Multi-orga
-
ウイルス感染による常在細菌叢の変容 Out of Control of Commensal BacteriaActivation of commensal bacteria by virus infection 常在細菌は人に害を与えることなく、場合によっては体に利益をもたらして共生しています。しかし、インフルエンザウイルス感染を要因として、下気道で常在菌が異常増殖し、二次性細菌性肺炎を引き起こします。 ウイルスと常在細菌はどのように相互作用するのだろう? わかっ...Activation of commensal bacteria by virus infection Commensal bacteria live in our body without causing harm or providing direct benefits. But, influenza virus infection triggers abnormal growth of commensal bacteria in lower respiratory tr
